Also, males and females were examined separately as well as combined. SES at birth was not found to be significantly associated with eGFR at age 63�C64 years, but this cannot be representative of the original cohort, due to the significant change in the proportion of participants who returned from each category. Loss of oestrogen due to the menopause is potentially of a greater contribution to kidney function in females than the variables tested in this study. However, oestrogen levels were not assessed in this study, so further research into this hypothesis would be needed. A further weakness when examining size at birth in comparison to eGFR is that data were only recorded for birth weight, rather than other indicators for size at birth, such as birth length, ponderal index and fetal weight-to-placental weight ratio index. However, standardised birth weight was used, which is a better measure of fetal growth than crude birth weight, but no association with eGFR was seen. While for many years, eGFR has been used in assessing renal function, 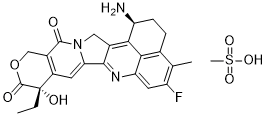 it has been shown to not be consistently associated with measured GFR across the normal range. How this may impact on the research findings in this and other studies remains to be seen. Renal disease urine protein was not measured as part of this study, so we are not able to assess whether this would add to the AbMole GSK 650394 hyperfiltration hypothesis. Perturbation of the oxidant/antioxidant balance within the cells has been suggested to be involved in the pathogenesis of several neurodegenerative disorders such as stroke, Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. These neurological disorders are associated with the production of abnormally aggregated proteins and belong to the group of protein conformational diseases. The altered aggregation of proteins in non-native conformation is generally associated with derangements of the endoplasmic reticulum and stress, which leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and excessive production of reactive oxygen species. When the rate of free radical generation exceeds the capacity of antioxidant defenses, oxidative stress ensues causing extensive damage to DNA, proteins and lipids. An increasing body of evidence suggests that dysfunction of cell energy metabolism is an important factor in neurotoxicity mediated by nitric oxide and that the intracellular content of thiols is crucial in determining the sensitivity of cells to oxidative and nitrosative stress. The actions of NO can be either direct, resulting from reactions between NO and specific biological molecules, or indirect, resulting from reactions of NO-derived reactive nitrogen species. For instance, the reaction of NO with superoxide produces the peroxynitrite anion and represents an important pathway of NO reactivity. Peroxynitrite is a powerful oxidant and can nitrate aromatic amino acid residues such as tyrosine to form nitrotyrosine. Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy is a rare hereditary systemic vasculopathy, caused by mutations in the NOTCH3 gene encoding.
it has been shown to not be consistently associated with measured GFR across the normal range. How this may impact on the research findings in this and other studies remains to be seen. Renal disease urine protein was not measured as part of this study, so we are not able to assess whether this would add to the AbMole GSK 650394 hyperfiltration hypothesis. Perturbation of the oxidant/antioxidant balance within the cells has been suggested to be involved in the pathogenesis of several neurodegenerative disorders such as stroke, Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. These neurological disorders are associated with the production of abnormally aggregated proteins and belong to the group of protein conformational diseases. The altered aggregation of proteins in non-native conformation is generally associated with derangements of the endoplasmic reticulum and stress, which leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and excessive production of reactive oxygen species. When the rate of free radical generation exceeds the capacity of antioxidant defenses, oxidative stress ensues causing extensive damage to DNA, proteins and lipids. An increasing body of evidence suggests that dysfunction of cell energy metabolism is an important factor in neurotoxicity mediated by nitric oxide and that the intracellular content of thiols is crucial in determining the sensitivity of cells to oxidative and nitrosative stress. The actions of NO can be either direct, resulting from reactions between NO and specific biological molecules, or indirect, resulting from reactions of NO-derived reactive nitrogen species. For instance, the reaction of NO with superoxide produces the peroxynitrite anion and represents an important pathway of NO reactivity. Peroxynitrite is a powerful oxidant and can nitrate aromatic amino acid residues such as tyrosine to form nitrotyrosine. Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy is a rare hereditary systemic vasculopathy, caused by mutations in the NOTCH3 gene encoding.
Monthly Archives: March 2019
As recorded by the health visitor increases rapidly from around the middle of the second trimester
Therefore, this developmental stage is crucial to kidney function, and animal studies have shown various factors can influence this stage, such as foetal nutrition. Factors affecting the normal progression of nephrogenesis during this “critical window” in foetal growth can change the structure of the kidney, the number of nephrons a person is born with and can potentially lead to For competitions carrying pBR322 or its derivatives bladders and kidneys have been also unfold onto ampicillin alterations in adult life kidney function. A number of studies have found a positive association between birth weight and eGFR, but others have found no association. However, the majority of these studies were conducted in children or young adults, and the oldest mean age for any of these studies was 49 years. The age at which these studies were conducted is important, as the effect of early life influences on kidney function may not become apparent until later in adult life. Further, little research has been done to investigate the impact of other early life influences in relation to adult kidney function such as socio-economic status and breastfeeding. Research into the associations between later life influences and kidney function have shown conflicting results for body mass index and smoking, and a positive association for current SES. The Newcastle Thousand Families birth cohort provided a unique opportunity to analyse longitudinal data and investigate the effects of both early and later life influences on kidney function at age 63�C64 years. The Newcastle Thousand Families study began as a prospective study of all 1142 children born in May and June 1947 to mothers resident in Newcastle upon Tyne, in northern England. The health, growth and development of the cohort were followed in great detail up to age 15 years. Throughout the first years of the children’s lives, all families were visited both on a routine and on an ad hoc basis by the study team, which consisted of health visitors and paediatricians. The cohort underwent a major follow-up at age 49�C51 years, and again at age 63�C64 years. In both follow-up waves, health and lifestyle questionnaires were sent out for completion and return and study members were invited to attend for clinical examination. The latest follow-up wave was conducted between 2010 and 2011, with 354 of the original 1142 participants returning for a clinical examination. There have been 183 known deaths in the cohort, including 2 from renal disease. Information on early life was recorded prospectively for all study members. Birth weights, as recorded by the midwife at the time of the child’s birth, were standardised for gestational age and sex. Socioeconomic 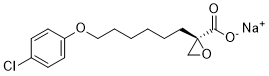 status at birth was measured by paternal occupational social class at the time of the child’s birth. Housing conditions were assessed by the city’s Public Health Department near the time of the child’s birth, and scored for the presence of overcrowding, lack of hot water, toilets shared between households and dampness or poor repair. Duration of being breast fed was defined as the length of time a study member was at least partly breast fed.
status at birth was measured by paternal occupational social class at the time of the child’s birth. Housing conditions were assessed by the city’s Public Health Department near the time of the child’s birth, and scored for the presence of overcrowding, lack of hot water, toilets shared between households and dampness or poor repair. Duration of being breast fed was defined as the length of time a study member was at least partly breast fed.
Our results showed resistant to almost all tested antimicrobials of the identified NDM-1-producing Ecoli isolate
In contrast, NBS1 uses the conserved C-terminal domain to interact with the subunits of PI3K to achieve its activation. Further structural analysis of co-crystalized NBS1 and the mTOR/Rictor/SIN1 complex will delineate the molecular interactions between these molecules. Our previous results showed that promote academic research health care benefits gprd increased NBS1 expression was constantly observed in different tumor samples, suggesting that increased NBS1 levels in tumor tissues may contribute significantly  to the increased Akt activity observed in different tumor samples. Our discovery points to the unique role of NBS1 in the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway using a newly identified internal domain to interact with the mTOR/Rictor/SIN1 complex to achieve activation. Antimicrobial resistance is a growing global challenge to human health. The emerging New Delhi metallo-b-lactamase, an acquired class B carbapenemase that was first clinically detected in a patient at a hospital in New Delhi, India, has brought up worldwide public attention again. It confers resistance to a broad-spectrum of b-lactams, including carbapenems, which are the mainstream treatment for antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. Although current reports indicate that NDM-1 does not hydrolyze monobactams, most of NDM-1-carrying strains also express enzymes that could hydrolyze monobactams, making NDM-1-producers very difficult to control. The rapid dissemination of NDM-1-producing gram-negative species also contributes to this major concern of public health. It has been reported in.50 countries across five continents, in the last 2 years. In contrast to most other countries where NDM has been mainly identified in Enterobacteriaceae, in China to date NDM has only been reported in Acinetobacter and Enterococcus faecium. However, other types of MBLs, such as IMP, and other classes of acquired carbapenemases, such a KPC, have been reported in Enterobacteriaceae in China, but isolates of NDM-1-producing E.coli have not previously been identified in China. NDM-1-harboring strains could be highly multidrug resistant. Previous reports on NDM-1-producing Acinetobacter spp. have demonstrated that strains resistant to all available antimicrobials except colistin were common in China. The patient had a good general condition and the infection was localized. Ultimately, the patient survived the infection. But this case should have raised public concerns again over increasing incidence of highly multidrug resistant NDM-1-harboring strains in China. Travelers contribute significantly to the global movement of microbes and resistance genes. Although nosocomial transmission of NDM-1 has occurred in many countries, medical tourism plays a significant role in the spread of NDM1, and traveling to the Indian subcontinent is a significant risk factor of infection with an NDM-1-producing bacterium. Patients in China who were found to have blaNDM-1-carrying bacteria had no history of traveling to the Indian subcontinent or another country.
to the increased Akt activity observed in different tumor samples. Our discovery points to the unique role of NBS1 in the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway using a newly identified internal domain to interact with the mTOR/Rictor/SIN1 complex to achieve activation. Antimicrobial resistance is a growing global challenge to human health. The emerging New Delhi metallo-b-lactamase, an acquired class B carbapenemase that was first clinically detected in a patient at a hospital in New Delhi, India, has brought up worldwide public attention again. It confers resistance to a broad-spectrum of b-lactams, including carbapenems, which are the mainstream treatment for antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. Although current reports indicate that NDM-1 does not hydrolyze monobactams, most of NDM-1-carrying strains also express enzymes that could hydrolyze monobactams, making NDM-1-producers very difficult to control. The rapid dissemination of NDM-1-producing gram-negative species also contributes to this major concern of public health. It has been reported in.50 countries across five continents, in the last 2 years. In contrast to most other countries where NDM has been mainly identified in Enterobacteriaceae, in China to date NDM has only been reported in Acinetobacter and Enterococcus faecium. However, other types of MBLs, such as IMP, and other classes of acquired carbapenemases, such a KPC, have been reported in Enterobacteriaceae in China, but isolates of NDM-1-producing E.coli have not previously been identified in China. NDM-1-harboring strains could be highly multidrug resistant. Previous reports on NDM-1-producing Acinetobacter spp. have demonstrated that strains resistant to all available antimicrobials except colistin were common in China. The patient had a good general condition and the infection was localized. Ultimately, the patient survived the infection. But this case should have raised public concerns again over increasing incidence of highly multidrug resistant NDM-1-harboring strains in China. Travelers contribute significantly to the global movement of microbes and resistance genes. Although nosocomial transmission of NDM-1 has occurred in many countries, medical tourism plays a significant role in the spread of NDM1, and traveling to the Indian subcontinent is a significant risk factor of infection with an NDM-1-producing bacterium. Patients in China who were found to have blaNDM-1-carrying bacteria had no history of traveling to the Indian subcontinent or another country.
Different subfractions of HDL cholesterol may affect cardiovascular outcomes differently
This study used questionnaires to exclude subjects who claimed to have exercised strenuously or regularly within 1 month before to the study. Resting energy expenditure measurements and 24-h activity monitoring will clarify this possibility. Moreover, it will be useful to test irisin levels both before and after exercise training. We have examined the irisin levels with both western blotting and an enzyme immunoassay kit, and confirmed the decreased levels of irisin in CKD patients. However, we noticed a discrepancy between the irisin levels detected by western blotting and enzyme immunoassay. The plasma samples used for these 2 different detection methods were processed differently. Plasma samples used for enzyme immunoassay were unprocessed, whereas those used for western blotting detection were deglycosylated and precleared of IgG and albumin. We believe these different sample preparation methods may have resulted in the discrepancy in irisin levels. The irisin levels detected with western blotting are more likely to be of the free form unbound to proteins. Future work on the protein-binding ratio of irisin and irisin metabolism would be needed to resolve these questions. This study has some limitations. Our strict patient selection criteria excluded patients with diabetes, liver function abnormalities, heart failure, stroke, systemic lupus erythematosus, and severe obesity. Therefore, the results of this study are not applicable to all CKD patients. Further, this study did not measure the subfractions of HDL cholesterol. The effect of irisin on HDL cholesterol composition warrants further study. Moreover, our study design did not allow us to infer the mechanism of action of irisin. Further therapeutic clinical trials or animal studies are necessary to clarify the mechanisms underlying the effects of irisin. It is also important to test if the changes in irisin levels correlate with the progression of CKD from stage 1 to stage 5. In summary, this study demonstrated that irisin levels are decreased in patients with CKD and are positively associated with HDL cholesterol concentration. Irisin may be a promising therapeutic agent for treating cardiovascular disease in CKD patients. Cell survival hinges on the ability to respond to extracellular stimuli and self-regulate in a changing environment. Intracellular dynamics are controlled by intricate arrays of biochemical networks, and in particular, the spatiotemporal dynamics of species concentrations are key to a number of processes, including cell signalling, pattern formation and morphogenesis. Quantifying the signal transmission properties of a network is key to understand how its connectivity and AbMole Povidone iodine parameters shape the conversion of signalling cues into cellular responses, as well as the detection of intervention points for engineering or therapeutic applications. Our goal in this paper is 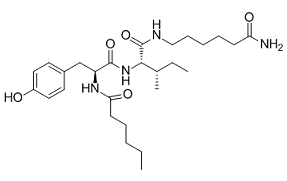 to provide tools for the mathematical quantification of signal transmission in biochemical networks. We use the time-integral of species concentrations as a proxy for the ability of a network to transmit input cues. It represents the cumulative effect of external stimuli on the chemical species and has been used to discover an input amplification phenomenon in the MAPK pathway, and to study the activation of cell membrane receptor such as the epidermal growth factor and the erythropoietin receptors. We focus on networks of biochemical reactions subject to molecular diffusion and spatiotemporal stimuli. We aim at obtaining exact formulae for the time-integrals of species concentrations. An analytic approach can reveal structural properties of the model under consideration, as opposed to simulation-based studies where it is unclear if predictions are rather a consequence of the particular parameter values examined.
to provide tools for the mathematical quantification of signal transmission in biochemical networks. We use the time-integral of species concentrations as a proxy for the ability of a network to transmit input cues. It represents the cumulative effect of external stimuli on the chemical species and has been used to discover an input amplification phenomenon in the MAPK pathway, and to study the activation of cell membrane receptor such as the epidermal growth factor and the erythropoietin receptors. We focus on networks of biochemical reactions subject to molecular diffusion and spatiotemporal stimuli. We aim at obtaining exact formulae for the time-integrals of species concentrations. An analytic approach can reveal structural properties of the model under consideration, as opposed to simulation-based studies where it is unclear if predictions are rather a consequence of the particular parameter values examined.
Klf2 and Klf5 can replace Klf4 in OSKM mediated reprogramming of somatic cells to iPS cells
Expression of hKlf4 in the mES cells was induced in the absence of Dox under two different conditions, one in the undifferentiated state maintained by LIF and the second in the RA induced differentiation condition treated for 1.5 days. The protein expression in cell extracts was detected by Western blot analysis. The avidin-HRP conjugate detected strong bands at the size corresponding to the biotinylated hKlf4 protein in the absence of Dox in both the LIF condition and the RA condition. Also, in all the samples, the avidin-HRP conjugate detected endogenous biotinylated proteins, the expression levels of which were lower than those of the induced biotinylated hKlf4 proteins. Western blot analysis using the antiBirA antibody detected the BirA bands in the absence of Dox in both the undifferentiated LIF condition and the differentiated RA condition. When Dox was present, the biotinylated hKlf4 protein and the BirA protein were almost undetectable, indicating that this regulatable in vivo biotinylation expression system was relatively tight. It has been reported that Klf4 expression is regulated by the LIF signaling pathway, thus the hKlf4 ES cell line was cultured in the presence or absence of LIF. As expected, in the presence of LIF, cells showed compact and undifferentiated morphology. In the absence of LIF, cells grew more flattened. After inducing forced  expression of hKlf4, within 12 hours, obvious differences in cell morphology were observed compared with the un-induced control. After two days of induction, the ES cells expressing hKlf4 grew less than the control cells. After four than the cells without induction of hKlf4. Cell proliferation assays showed that after one day of induction the cell numbers of the hKlf4 expressing cells were around two-fold lower than those of the Dox+ control cells, and after three days of induction the cell numbers of the hKlf4 expressing cells were around 10-fold fewer than those of the Dox+ control cells. Therefore, hKlf4 induction strongly affected cell growth and viability in the presence or absence of LIF. The effects of expression of hKlf4 in mES cells on gene expression were analyzed. Gene expression was quantified by realtime RT-qPCR. Cells were harvested after induction for 1.5 days. Recombinant hKlf4 mRNA expression was detected using specific hKlf4 qPCR doppler echocardiography evaluating aortic velocity primers. In the absence of Dox, hKlf4 mRNA was highly induced, and in contrast, in the presence of Dox, hKlf4 mRNA was almost undetectable. Total Klf4 mRNA, including transgene hKlf4 mRNA and endogenous mKlf4 mRNA, was detected by specific conserved total Klf4 primers. As expected, in the control Dox+ ES cells, total Klf4 was expressed at high levels in the presence of LIF, and expressed at low levels in the absence of LIF. In the Dox2 hKlf4 expressing ES cells, total Klf4 was expressed significantly higher than total Klf4 in the Dox+ control cells. In addition, endogenous mKlf4 mRNA was detected by specific mKlf4 primers. In the Dox2 hKlf4 expressing ES cells, endogenous mKlf4 was expressed significantly lower than in the Dox+ control cells, suggesting that endogenous mKlf4 was repressed by the induction of hKlf4, and that endogenous mKlf4 was auto-regulated to prevent its overexpression. Several Klf family members, Klf2, Klf4 and Klf5, are expressed in mES cells and down-regulated during mES cell differentiation. Klf2, Klf4 and Klf5 cooperatively bind to target genes and regulate their expression. In the Dox2 hKlf4 expressing ES cells, Klf2 and Klf5 were expressed significantly lower than those in the Dox+ control cells, suggesting that they were repressed by the induction of hKlf4. It has been demonstrated that Esrrb can replace Klf4 in OSKM mediated somatic cell reprogramming. Esrrb and Klf4 have many common targets.
expression of hKlf4, within 12 hours, obvious differences in cell morphology were observed compared with the un-induced control. After two days of induction, the ES cells expressing hKlf4 grew less than the control cells. After four than the cells without induction of hKlf4. Cell proliferation assays showed that after one day of induction the cell numbers of the hKlf4 expressing cells were around two-fold lower than those of the Dox+ control cells, and after three days of induction the cell numbers of the hKlf4 expressing cells were around 10-fold fewer than those of the Dox+ control cells. Therefore, hKlf4 induction strongly affected cell growth and viability in the presence or absence of LIF. The effects of expression of hKlf4 in mES cells on gene expression were analyzed. Gene expression was quantified by realtime RT-qPCR. Cells were harvested after induction for 1.5 days. Recombinant hKlf4 mRNA expression was detected using specific hKlf4 qPCR doppler echocardiography evaluating aortic velocity primers. In the absence of Dox, hKlf4 mRNA was highly induced, and in contrast, in the presence of Dox, hKlf4 mRNA was almost undetectable. Total Klf4 mRNA, including transgene hKlf4 mRNA and endogenous mKlf4 mRNA, was detected by specific conserved total Klf4 primers. As expected, in the control Dox+ ES cells, total Klf4 was expressed at high levels in the presence of LIF, and expressed at low levels in the absence of LIF. In the Dox2 hKlf4 expressing ES cells, total Klf4 was expressed significantly higher than total Klf4 in the Dox+ control cells. In addition, endogenous mKlf4 mRNA was detected by specific mKlf4 primers. In the Dox2 hKlf4 expressing ES cells, endogenous mKlf4 was expressed significantly lower than in the Dox+ control cells, suggesting that endogenous mKlf4 was repressed by the induction of hKlf4, and that endogenous mKlf4 was auto-regulated to prevent its overexpression. Several Klf family members, Klf2, Klf4 and Klf5, are expressed in mES cells and down-regulated during mES cell differentiation. Klf2, Klf4 and Klf5 cooperatively bind to target genes and regulate their expression. In the Dox2 hKlf4 expressing ES cells, Klf2 and Klf5 were expressed significantly lower than those in the Dox+ control cells, suggesting that they were repressed by the induction of hKlf4. It has been demonstrated that Esrrb can replace Klf4 in OSKM mediated somatic cell reprogramming. Esrrb and Klf4 have many common targets.